The third population of the globe has signs of hypertension. The pressure with hypertension causes stenosis and vascular damage, and sometimes hemorrhagic heart attack. Therefore, even healthy people are extremely important to know what pressure is, what affects it, what indicators can be considered the norm, which numbers on the tonometer should serve as a signal for the beginning of treatment.
The essence of the concept
Blood pressure is due to the power of its effect on the main and peripheral vessels. Pressure indicators are directly dependent on several factors:
- vascular elasticity;
- heart contractions;
- The volume of blood pumped with heart for a certain period of time.
The value of blood pressure (blood pressure) is customary to write in the form of a relationship in which:
- The upper digit, large - systolic pressure (with a contraction of the heart);
- The lower digit, smaller - diastolic pressure (between heart contractions).
Blood pressure can change - with a change in body position, during physical exercises, with nervous overstrain, at rest or after eating. If a person does not experience health problems, after a short time the pressure is stabilized. With hypertension, its increased indicators are preserved for quite some time. In hypertensive patients, sharp fluctuations in blood pressure are observed. Normal after sleep, after eating it can rise, then decline. Evening pressure indicators usually exceed the morning, and at night they sometimes drop sharply.
Analyzing blood pressure indicators, more value is usually attached to the upper number. It is increased systolic pressure that the main risk factors for the development of cardiovascular pathologies in patients are over 50 years old. In the vast majority of people, it increases over the years-due to the fact that the main arteries lose their elasticity and expose atherosclerotic plaques.
Norm and pathology
Blood pressure is an individual indicator, depending on the age, surrounding conditions, accompanying pathologies, and even from the time of day. But there are averaged medical indicators. Having found out what pressure the patient has, the doctor determines - Hypertension is or variant of the norm.
Blood pressure in patients over 18 years old
| Pressure | Indicators, mm Hg. Art. | Indicators, mm Hg. Art. |
|---|---|---|
| Systolic | Diastolic | |
| Optimal | Less than 120 | Less than 80 |
| Normal | Up to 130 | Up to 85 |
| Normally tall | Up to 140 | Up to 90 |
| 1 degree of hypertension | Up to 160 | Up to 100 |
| 2 degree of hypertension | Up to 180 | Up to 110 |
| 3 degree of hypertension | Over 180 | Over 110 |
| Isolated systolic hypertension | Over 180 | Less than 110 |
Systematic pressure control will help to avoid the serious consequences of hypertension, since pathological changes in indicators will be seen in a timely manner.
Reasons for deviation from the norm
Blood pressure never changes for no reason. Its fluctuations can be caused by diseases of the cardiovascular, digestive, genitourinary system, traumatic brain injuries. But not always factors provoking the change are due to pathologies. The growth of blood pressure indicators often occurs due to:
- allergic reactions;
- stressful situations;
- hormonal failures;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuses;
- weather dependence;
- taking some drugs;
- overwork;
- dehydration;
- eating fatty foods;
- excessive amount of salt consumed;
- Hypodynamia or, on the contrary, physical strain.

The reason for increasing pressure may be age -related changes in the body and hereditary predisposition.
Clinical manifestations
The increased blood pressure is very noticeable. Visual symptoms of pathological changes are more likely to serve:
- Acute headache (usually in temples and back of the head), often accompanied by vomiting reflexes;
- redness of the skin (sometimes vessels appear);
- pronounced weakness, noise in the ears, flies in front of the eyes;
- redness of eye proteins (sometimes violation of visual acuity);
- dyspnea;
- pain behind the sternum;
- chills;
- insomnia;
- heart heartbeat;
- increased sweating.
In the presence of such symptoms, consult a doctor. Early hypertension is dangerous asymptomatic. A person sometimes does not even think about the fact that he can have increased pressure.
With increased pressure in the diet, it is necessary to include products that can effectively break down fats and prevent thrombosis.
Diagnosis of changes
After 20 years, it is recommended to measure the pressure during examinations. If it is higher than the norm, the doctor prescribes additional tests. One -time high indicators do not always indicate the presence of hypertension. The disease is diagnosed if increased indicators are observed with several consecutive examinations, as well as if they are preserved after three -month compliance with the doctor’s instructions to adjust the lifestyle.
Self -diagnosis on the pulse
Without a medical device, it is impossible to accurately determine pressure indicators, but the presence of negative changes can be assumed by the pulse. By applying the ring and index fingers to the carbon artery, the number of bends of the heart in 30 seconds should be calculated and multiply the resulting figure by two (the number of beats per minute). The pulse equal to 60-80 shots is considered normal. With increased pressure, the pulse is felt without difficulty. If there is a heart rate monitor, you can use it.

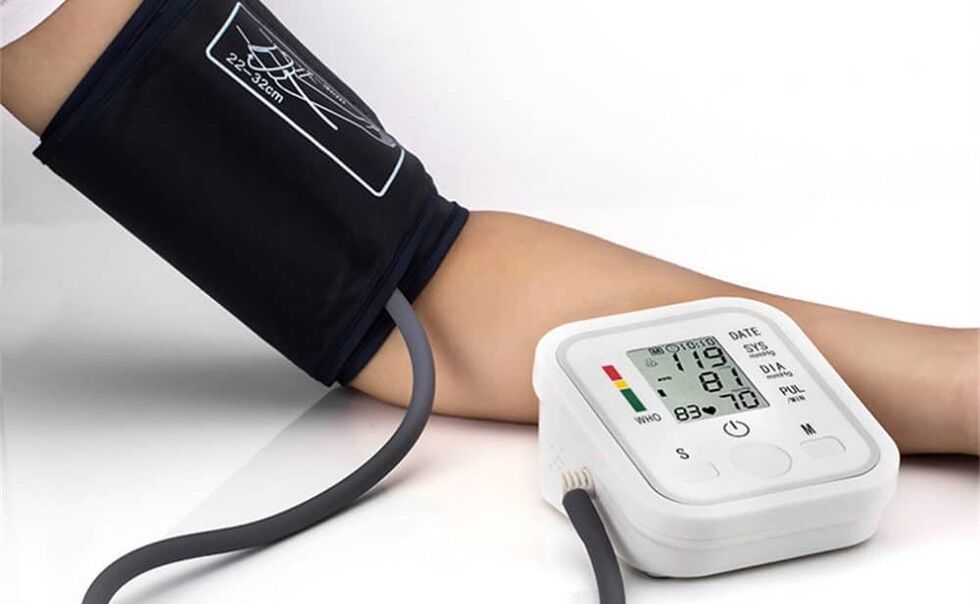
Using a tonometer
For accurately measuring blood pressure, various kinds of tonometers are used. The structures of the device are distinguished by the principle of action. Mercury tonometers were replaced by pneumatic and then electronic devices. The latter can easily use any person who does not even have a medical education. They are characterized by compactness, accuracy and ease of use.
Typically, such tonometers show not only systolic and diastolic pressure indicators, but also the pulse frequency. At the same time, the previous measurements are "remembered" by which experts monitor the dynamics of changes in blood pressure indicators in each specific patient.
ARIMISTION RIGHTS
The measurement of blood pressure must be approached with maximum attention. This applies to both specialists and the patients themselves who independently monitor the level of pressure. There are certain rules:
- The day before measurement, you need to abandon tonic drinks and smoking;
- On the day of measurement, you should not use eye and nasal drops;
- measure pressure half an hour after eating;
- Before applying the tonometer cuff, the patient should take a convenient position by putting a relaxed hand on a flat hard surface;
- The cuff must be placed in the middle of the shoulder. From below its edge should be 2. 5 cm from the elbow deepening. Air tubes should lie along the midline of the shoulder;
- between the cuff, located on the same level with the heart, and the shoulder should be left the gap into which the finger is easily placed;
- During the tonometer operation, absolute calm should be maintained.
First, experts recommend measuring pressure on both hands, then only on the one that "gives out" the highest indicators. If the measurement is carried out outside the walls of the medical institution, the patient is recommended to make an "accounting" notebook and enter the day, time and measurements. How often to make measurements, the doctor determines.
Possible consequences
High blood pressure with hypertension is fraught with hypertensive crises- sudden jumps of indicators to critical. Such states provoke a sharp expansion of blood vessels that may break. In a series of consequences, hypertension is distinguished:
- problems with eyes (reduction of visual acuity, hemorrhage);
- renal failure;
- ischemia of the heart;
- heart failure;
- angina pectoris;
- stroke;
- infarction;
- impotence;
- swelling of the light and brain;
- death.
At the risk of exfoliating aneurysm of aorta, it is recommended to knock down the pressure as quickly as possible. And with cerebral disorders, this should be done without haste, otherwise they will aggravate.
High blood pressure often causes disability and even the death of the patient.
Home reaction
With hypertensive crisis (the upper pressure above 200 mm Hg), you need to urgently call an ambulance team and, before its arrival, begin to take measures to eliminate the symptoms. With a moderate increase in pressure, you can act independently.
Warning measures
If signs of increased pressure occur, it is necessary to measure its indicators. Headache, nausea, weakness can occur for other reasons. If the pressure is really increased, it follows:
- ensure peace, dimming and silence (including at the workplace);
- provide access for fresh air;
- to lie down, raising your head (at work, if there is no way, sit comfortably);
- do breathing exercises (diaphragmatic breathing focused on exhalation);
- massage the collar zone and head (it is desirable that relatives or friends do this);
- Drink a diuretic broth (parsley, lingonberry, green or kidney tea, rosehip).
Such measures lower the pressure slowly and are more likely to prevent the development of complications. If they do not help, you need to contact a cardiologist.
Quick effect
Patients with an active lifestyle often face the problem of rapid reduction in pressure. Drug drugs can do this, but they should be used carefully - in order to avoid an overdose, too quickly reduced pressure and other complications. The attending physician must prescribe medicines. Pressure quickly and safely reduce the pressure will help:
- peace;
- cooling compress on the head;
- Warm baths for limbs (not hot! ). You can use a container with water or a heating pad, mustard;
- Salting phytochai (valerian, motherwort, chamomile, mint, lemon balm).
In the absence of the expected effect, the listed measures are supplemented with drugs.
Homemade first -aid kit
With regularly emerging problems with pressure in the composition of the home medicine cabinet, special drugs should always be.
The absence of drug drugs can be compensated by the use of a "constant" drug, but its effect will be noticeable only after an hour or two after taking. Accepting pharmaceuticals, follows:
- use only the funds prescribed by the doctor;
- Do not mix drugs;
- dissolve "emergency care" tablets, and not swallow;
- Take the medicine lying (after taking, remain in a horizontal position for another 30 minutes). If necessary, you should get up slowly.
When accepting pharmaceuticals, it is necessary to pay attention to contraindications and side effects.
Inevitable restrictions
With increased pressure in order to avoid the development of negative consequences, it is necessary to adhere to certain restrictions:
- Within 24 hours after stabilization of pressure, avoid increased physical activity;
- avoid psycho -emotional overloads, with the inevitable occurrence of stressful situations, take sedatives;
- Refuse the use of alcohol, caffein -containing drinks and smoking.
It should be excluded from the diet for fatty and too salty foods (smoked meats, canned food - including). After normalizing the pressure for a couple of days, the amount of fluid consumed should be limited.
The treatment of hypertension depends on the type of increased pressure, as well as the phases of the pathological process. It is possible to use combined and monotherapy. After thorough diagnosis and prescribing drugs, the cardiologist will give recommendations for maintaining pressure in normal, as well as on measures that are needed when it has a sharp increase.